Source: Cointelegraph
Web3 and Web 3.0 are terms often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to two different concepts. Web3 refers to a decentralized web that is based on blockchain technology, while Web 3.0 is a semantic web that is more intelligent and connected.
Web3 coinage
The term “Web3” was first coined by Gavin Wood, co-founder of the Ethereum blockchain, in 2014. Wood used the term to describe a vision for a decentralized web that is not controlled by any single entity. Wood’s vision for Web3 is based on blockchain technology, which he believes can be used to create a more secure, transparent and equitable web.
Web3 principles
Both Web3 and Web3.0 technology-driven paradigms have guiding principles and have certain building blocks that they rely on. These are explained below:
- Decentralization
Web3 is decentralized, meaning it is not controlled by any single entity. Instead, it is powered by a network of computers that are distributed all over the world. This makes Web3 more secure and resistant to censorship. - Blockchain-based
Web3 is based on blockchain technology. Blockchain is a distributed ledger system that is used to record transactions in a secure and transparent way. This makes Web3 well-suited for applications such as financial transactions and supply chain management. - Cryptocurrencies
Web3 is powered by cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography. They are units of shared value in a decentralized ecosystem. This makes cryptocurrencies ideal for use in Web3 applications.
Web 3.0 coinage
The term “Web 3.0” was first coined by Tim O’Reilly, founder of O’Reilly Media, in 2006. O’Reilly used the term to describe a vision for a more intelligent and connected web that is based on semantic web technologies. O’Reilly’s vision for Web 3.0 is a web where machines can understand the meaning of data and where users can interact with the web in a more natural and intuitive way.
Web 3.0 principles
Web 3.0 principles include:
- Semantic
Web 3.0 refers to a semantic web, and it is essentially designed to make machine-readable data more accessible and useful. This will enable computers to understand the meaning of data and to use it in more intelligent ways. - Connected
Web 3.0 is designed to be more connected than the current web. This means that data will be more easily shared and linked across different websites and platforms. This will make it easier for users to find the information they need and for developers to create new and innovative applications. - Open
Web 3.0 is designed to be an open web, accessible to everyone and built on open-source standards. This will make Web 3.0 more transparent and hold participants accountable for their actions.
Differences between Web3 and Web 3.0
The significant difference between Web3 and Web 3.0 is their focus. Web3 is focused on decentralization and security, while Web 3.0 is focused on intelligence and connectivity. Web 3.0 envisions a highly intelligent web that fosters seamless communication between various apps and services by enabling machines to comprehend and interpret information.
Another difference is the technologies they use. Web3 is based on blockchain technology, while Web 3.0 is based on semantic web technologies. To build trust and security in online interactions, decentralized ledgers, smart contracts and cryptographic principles are used in Web3. On the contrary, Web 3.0 makes use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning and natural language processing to comprehend and respond intelligently to user queries and requests.
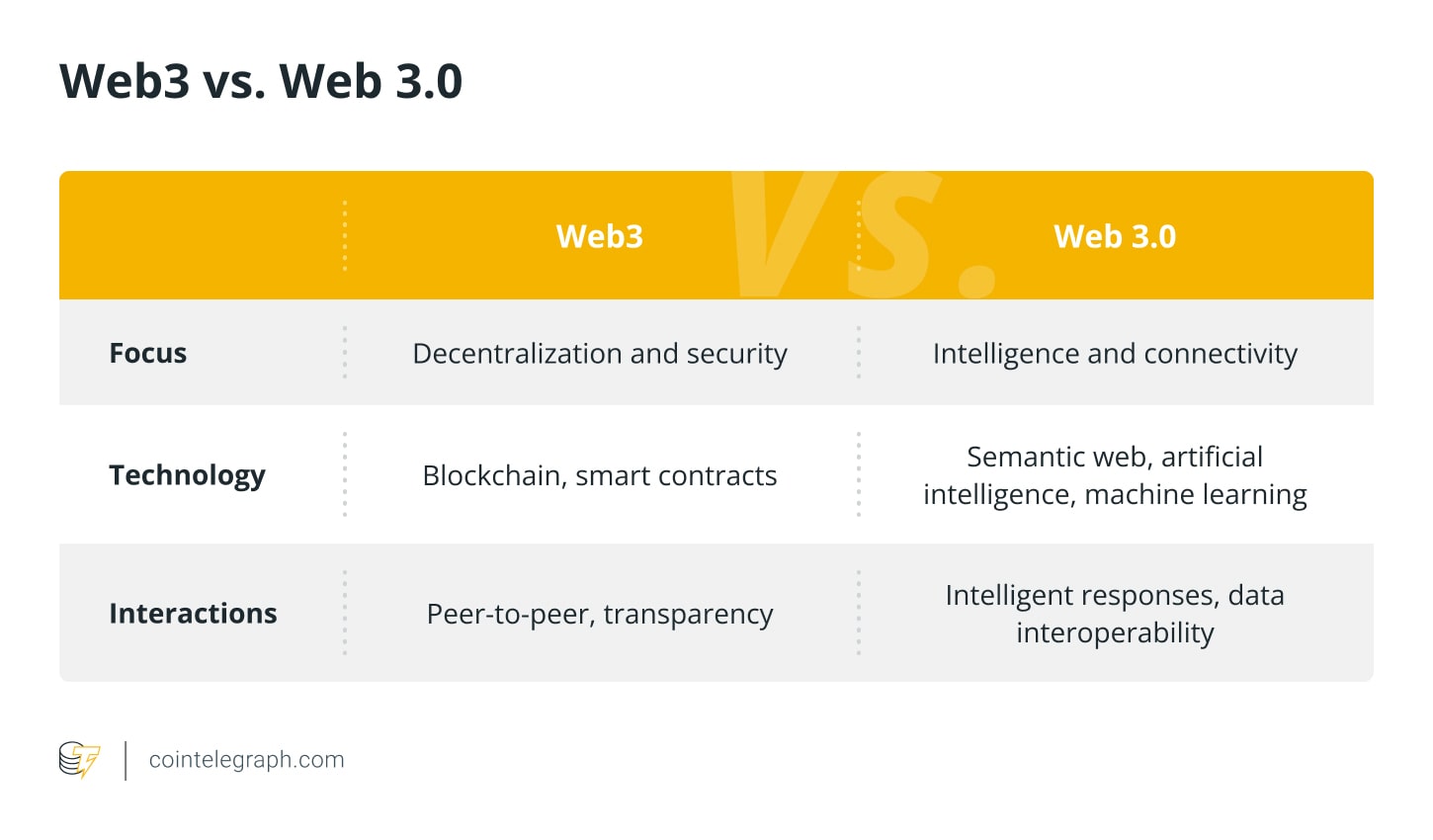
Finally, Web3 is still in its early stages of development, while Web 3.0 is still a concept being researched and developed. Researchers and tech pioneers are exploring how to combine decentralized, Internet of Things and AI technologies to build an intelligent and interconnected web.
Examples of Web3 and Web 3.0 applications
Here are some examples of Web3 and Web 3.0 applications:
Web3 applications
- Decentralized finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a financial system that is built on blockchain technology. DeFi applications allow users to borrow, lend, trade and invest assets without a central authority. - Nonfungible tokens (NFTs)
NFTs are digital assets that are unique and cannot be replaced. NFTs are often used to represent ownership of digital art, collectibles and gaming items. - Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are organizations that are governed by smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are stored on a blockchain. DAOs allow users to collaborate and make decisions without a central authority.
Web 3.0 applications
- Voice assistants
Voice assistants such as Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant are examples of Web 3.0 applications. Voice assistants use machine learning to understand human language and to provide users with information and services. - Lifestyle engines
Personalization engines like those used by Netflix and Amazon recommend products and content to users based on their past behavior. Personalization engines use machine learning to understand user preferences and to make recommendations that are more likely to be of interest to users. - Semantic search engines
Semantic search engines such as Google Search are evolving to become more intelligent and to better understand the meaning of search queries. Semantic search engines can now provide users with more relevant and comprehensive results.
Web 3 and Web 3.0: Convergence debate
In essence, while conceptually Web3 and Web 3.0 can mean different things, proponents believe they will eventually converge as decentralized technologies become more intelligent and intelligent applications become more decentralized. Others believe that Web3 and Web 3.0 will remain distinct concepts, each focusing on unique strengths.
Therefore, predicting the convergence or divergence of Web 3.0 and Web 3.0 is a difficult endeavor because the future trajectory of both technologies is still unknown. The evolution of technology is inherently unpredictable and is impacted by a wide range of factors, including user acceptance, governmental regulations and scientific advancements. As a result, it’s imperative to approach these concepts with an open mind, appreciating the possibilities when leaning toward any particular viewpoint.